Excel is a powerhouse tool for data management and analysis. Among its arsenal of functions, the VLOOKUP function reigns supreme, allowing users to fetch and manipulate data with precision.

What is the VLOOKUP Function?
VLOOKUP, an abbreviation for Vertical Lookup, is an Excel function that enables users to search for a specific value in a column and retrieve related information from the same row within a different column. This function is a game-changer in simplifying data analysis and streamlining processes across various industries.
Applying VLOOKUP in Real-Life Scenarios
Imagine a sales dataset containing product codes, prices, and corresponding sales figures. The VLOOKUP function becomes invaluable in swiftly retrieving the price of a specific product based on its code, empowering businesses to make informed decisions.
Syntax: The syntax for VLOOKUP in Excel is
=VLOOKUP(lookup_value, table_array, col_index_num, [range_lookup])
Practical example:
Example: Using VLOOKUP for Sales Data Analysis
Consider a spreadsheet with columns for Product ID, Product Name, and Sales Price. To find the price of a product with a given ID, follow these steps:
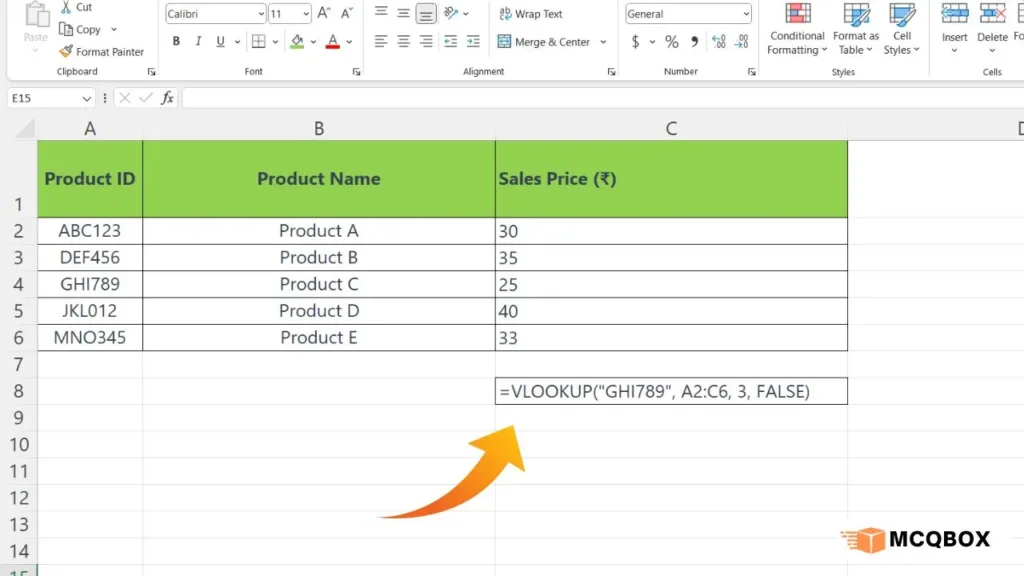
Suppose we want to find the sales price of “Product C” with the Product ID “GHI789”. In an Excel cell, the VLOOKUP formula would look like this:
=VLOOKUP(“GHI789”, A2:C6, 3, FALSE)
Here, “GHI789” is the lookup_value (Product ID), A2:C6 is the table_array encompassing the dataset, 3 represents the column index containing the sales price, and FALSE ensures an exact match.
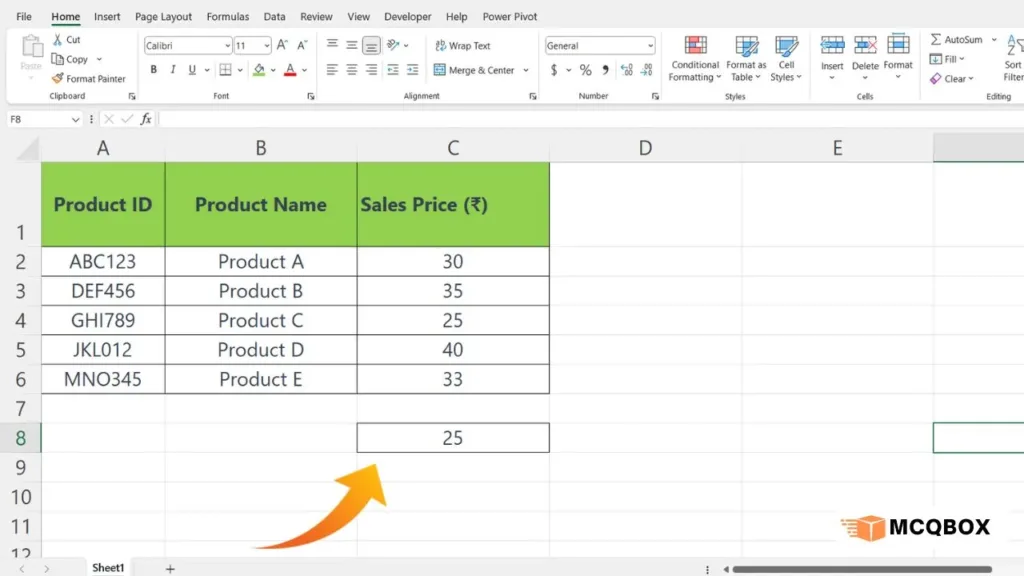
After entering this formula in a cell, Excel will locate the matching Product ID (“GHI789”) in the table and display the corresponding sales price (₹ 25) in the cell where the formula is placed.